10 AI In Manufacturing Trends To Look Out For In 2024
Artificial intelligence (AI) is slowly being used in manufacturing facilities. Thanks to AI advancements, we can now do tasks like predictive maintenance, cognitive computing, swarm intelligence, context-aware computing, smart machines, hardware accelerators, and generative design.
Automated image recognition is used throughout the BMW Group for quality control and inspections, as well as the removal of pseudo-defects (deviations from target despite no genuine flaws). Because of this, their production is extremely precise.
Porsche is yet another manufacturer to reap the benefits of AI technology. Significant amounts of the automobile production process are automated with the use of autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs).
Other applications of AI in production include more accurate demand forecasting, heightened quality control, enhanced inspections, and automated stockrooms. “Industry 4.0,” the movement toward more automation in manufacturing plants and the massive creation and transfer of data, relies heavily on artificial intelligence.
What is the AI trend in the manufacturing industry?
AI will contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the manufacturing industry by 2025.
 The graph has been taken from Google Cloud which explains the top three manufacturing sectors deploying AI. Artificial intelligence can revamp the manufacturing sector. Possible benefits include higher output, lower costs, better quality, and less downtime. This technology can be used in a variety of settings, including large industries. AI simplifies industrial operations by fully automating complicated jobs and requiring fewer people to maintain. It also provides the flexibility necessary for organizations to respond swiftly to changes in demand or product specifications by revising production plans or rerouting materials.
The graph has been taken from Google Cloud which explains the top three manufacturing sectors deploying AI. Artificial intelligence can revamp the manufacturing sector. Possible benefits include higher output, lower costs, better quality, and less downtime. This technology can be used in a variety of settings, including large industries. AI simplifies industrial operations by fully automating complicated jobs and requiring fewer people to maintain. It also provides the flexibility necessary for organizations to respond swiftly to changes in demand or product specifications by revising production plans or rerouting materials.
How large is the AI market in manufacturing?
 This graph has been taken from Deloitte. AI in manufacturing would rise from its 2023 level of USD 5,070 million to a whopping USD 68,360 million by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 33.5%.
This graph has been taken from Deloitte. AI in manufacturing would rise from its 2023 level of USD 5,070 million to a whopping USD 68,360 million by 2032, expanding at a compound annual growth rate of 33.5%.
- In 2022, the market share for North America was the highest. Between 2023 and 2032, Asia-Pacific economies are projected to expand at an exceptional CAGR.
- In 2022, software made well over 32% of Offering’s total revenue.
- From 2023 to 2032, the computer vision technology subsegment is anticipated to grow at the highest compound annual growth rate (CAGR).
- Between 2023 and 2032, the Application market is expected to be led by the predictive maintenance and machinery inspection subsegment.
- Between 2023 and 2032, the market for medical devices is expected to grow at the fastest rate of any industry.
What role is AI playing in the future of manufacturing?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the industrial sector by increasing efficiency and allowing for more precise quality management. Because it can handle massive volumes of data in real-time, make choices on the fly, and automate procedures, AI is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry.
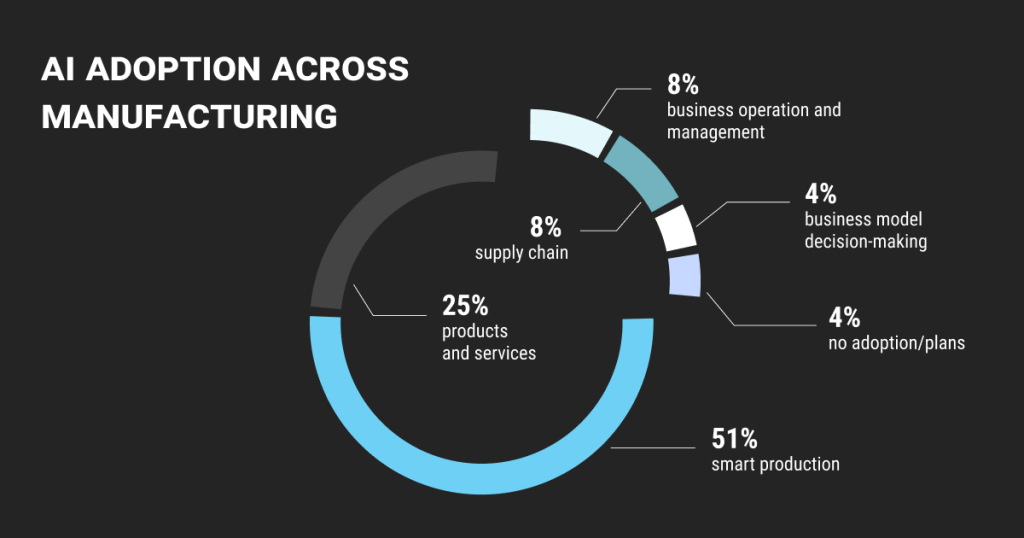 Artificial intelligence (AI) is being implemented in factories to reduce the frequency and length of downtime. Artificial intelligence may be used in many different ways in the industrial industry. Such applications might be generalized as smart manufacturing, corporate operations, supply chain, and decision-making. The increased use of AI in manufacturing has improved my company’s capacity for strategic planning, supply chain management, and overall operation management. Using artificial intelligence, manufacturing companies with R&D programs may cut down on the time and money spent on conventional operational procedures.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is being implemented in factories to reduce the frequency and length of downtime. Artificial intelligence may be used in many different ways in the industrial industry. Such applications might be generalized as smart manufacturing, corporate operations, supply chain, and decision-making. The increased use of AI in manufacturing has improved my company’s capacity for strategic planning, supply chain management, and overall operation management. Using artificial intelligence, manufacturing companies with R&D programs may cut down on the time and money spent on conventional operational procedures.
The adoption of cutting-edge technical solutions like analytics, augmented reality, virtual reality, smart packaging, and additive manufacturing is driving the growth of artificial intelligence (AI) in the manufacturing market. In the future, businesses in sectors presently undergoing digital transformation are predicted to use AI-based services. Important elements contributing to the expansion of AI in the industrial market are the sector’s inherent resilience and the need for long-term solutions from businesses operating in it.
Read the Latest blog from us: AI And Cloud- The Perfect Match
What are some specific examples of AI being used in manufacturing?
- Cobots work with humans.
- RPA tackles tedious tasks.
- Digital twins help boost performance.
- Predictive maintenance improves safety, and lowers costs.
- Machine learning algorithms predict demand.
- Inventory management prevents bottlenecks.
- AI autonomous vehicles
- AI for factory automation
- AI in design and manufacturing
- AI-based connected factory
- AI-based visual inspections and quality control
- AI for purchasing price variance
10 Predictions for Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Manufacturing Domain in 2024
McKinsey claims that businesses who adopt AI see increased profits and decreased expenses. While 18% of respondents observed a rise in income of 6-10%, 16% noted a drop in expenses of 10-19%.
Trend 1: Artificial intelligence is being used to automate manufacturing processes.
When AI is added to robots, they may take over activities that need extreme precision. Using smart technology, many factories have reduced production costs, improved worker safety, and boosted productivity. Artificial intelligence (AI) can help manufacturers cut down on labor expenses while simultaneously raising plant output and efficiency. In addition, there are uses for:
- Implement elaborate plant automation systems
- Create a consolidated store for all operational data and context, making staff moves easier.
- Minimize the amount of inputs required to maintain production.
- Increase or decrease output quickly in response to changes in demand or manufacturing tactics.
Siemens is a leader in manufacturing automation. The two businesses have joined forces to boost factory output with the use of computer vision, cloud analytics, and AI algorithms. The Japanese automation firm Fanuc also employs robots with artificial intelligence to run its production lines. The robots can make crucial parts for CNC and motors, keep the factory floor’s gear running nonstop, and keep an eye on everything at all times.
Trend 2: Using AI to Determine Quality
The industrial sector has the greatest demand for AI in quality control. It turns out that even factory robots may get it wrong sometimes. Despite being very rare compared to humans, the costs associated with releasing flawed items to the market can add up. When applied to manufacturing processes, AI and ML combine human intellect with potent technology to bring about revolutionary breakthroughs.
Artificial intelligence (AI) can spot problems in machinery or products that a robot would miss. Using technology like cameras and Internet of Things sensors, AI software may examine products to automatically discover problems. The computer may then decide what to do with faulty items automatically.
- The final product’s quality and functionality benefit from this to a greater extent because of it. This is the major motivation for the widespread use of AI-powered automation and robust tools by many manufacturers in the detection of process or product design problems in the present day. By doing rigorous quality testing using AI, manufacturers ensure high-quality goods with a quicker time to market.
- BMW employs automatic image recognition for quality control, inspections, and the removal of pseudo-problems (variations from the target notwithstanding the absence of real defects). This has led to increased accuracy in their production methods.
Trend 3: NLP
- The development of NLP is facilitating workers’ ability to report problems and find answers to customer inquiries.
- The use of chatbots fueled by natural language processing (NLP) is a significant AI development with significant potential to enhance the effectiveness of factory problem reporting and assistance requests.
- This subfield of AI focuses on creating convincing simulations of human communication. Artificial intelligence can improve the quality, timeliness, and thoroughness of reports submitted by workers if they can utilize their mobile devices to speak with chatbots and report difficulties. This improves worker responsibility while lessening the burden on managers.
Trend 4: Using AI/ML/deep learning to boost prediction precision
Artificial intelligence (AI) in supply chain and logistics has great promise for facilitating real-time forecast updates and improved decision-making in the manufacturing industry. Planning and forecasting need to be more sophisticated and sensitive to disturbances. Machine learning and deep neural networks are being used by manufacturers to cut down on transactions while improving output. They hope that by replacing time-consuming processes like scanning with AI, they can speed up pallet preparation and improve packing accuracy.
The French food producer Danone Group is a perfect case. Danone has accomplished this by implementing ML into its demand forecasting procedures the following:
- Errors in forecasting have decreased by 20%.
- Sales decline by 30%
- Demand planners’ task has been cut in half.
Thales SA is yet another illustration. They have been using ML to forecast upkeep for Europe’s high-speed train systems. The organization collects data on the present and historical health of subsystems and thousands of sensors across Europe’s intercity rail networks. To achieve a high degree of dependability, it has built an AI system based on the data to detect probable problems and determine when certain parts need to be replaced.
Read: AI and Machine Learning Are Changing Business Forever
Trend 5: AI is accelerating progress toward the Sustainable Development Goals.
BCG found that AI may save between $1.3 trillion and $2.6 trillion in income and cost reductions while reducing greenhouse gas emissions by between 2.6 and 5.3 gigatonnes of CO2. Artificial intelligence and analytics will be used by businesses to determine their carbon footprints and identify areas for improvement.
The benefits of AI extend beyond the reduction of greenhouse gas output. Waste prevention measures including those aimed at decreasing ocean plastic litter and the creation of environmentally friendly goods and production processes are two more. Furthermore, manufacturing organizations must find a balance between operational efficiency and the dangers to corporate assets and people. Improvements in video analytics and building management systems have allowed businesses to leverage AI and analytics to make their workplaces safer for employees.
Due to the high cost of time, money, and resources, as well as the need to train a new generation of workers, it is essential for manufacturers to keep up with the latest developments in AI and incorporate them into their operations as soon as feasible.
The window of opportunity to integrate AI into production processes is closing fast for those who haven’t done so before.
Trend 6: Predictive analytics
The ability of AI to accurately forecast outcomes is still crucial, no matter how widespread the use of AI solutions becomes. Anticipating when the running machinery could break and preparing the necessary repairs in advance, enables manufacturers to avoid any future problems. Predictive analytics is also used in software that predicts the price of raw materials.
Trend 7: Creative pattern making
Businesses in the manufacturing sector may employ cloud computing and AI to create and improve 3D models. Here, ML models mimic the design process utilized by engineers, letting factories quickly develop a plethora of design options for a given product. The quality and speed of data collection is a major obstacle to integrating AI in manufacturing. To produce reliable inferences and judgments, AI models require vast amounts of information.
The reliability of the findings obtained is dependent on the quality and timeliness of the data utilized. Improving operational efficiency and productivity is a major benefit of using AI in manufacturing. Intelligent automation solutions driven by AI algorithms may improve efficiency in manufacturing, streamline logistics, and cut down on downtime.
Trend 8:Assurance of Quality
This is especially important in manufacturing since it guarantees a constant standard of quality across the board. Most faults are readily apparent to the human eye, making computer vision a powerful tool for artificial intelligence.
Foxconn, a contract manufacturer for Apple, Nintendo, Nokia, and Sony, among others, has successfully adopted Google Cloud Visual Inspection AI to improve quality control in its factories and cut down on QA costs.
Trend 9:Automatic, robotic execution of processes.
Robots used in industry, often known as industrial robots, are programmed to do repetitive tasks automatically, considerably reducing the likelihood of human mistakes. They shift the emphasis of human labor to more profitable activities.
Case in point, Schneider Electric, a French multinational specializing in digital automation and energy management, deployed RPA to minimize non-value-added jobs, saving time for staff to emphasize customer satisfaction.
Trend 10:Data Science for Warehousing
Artificial intelligence may be used to automate several tasks in warehouse management. Thanks to the constant stream of data they gather, manufacturers can keep a close check on their stockrooms and optimize their operations.
Automating quality control and inventory may boost productivity, save labor costs, and reduce the number of personnel needed to manage a warehouse. As a consequence, manufacturers may increase their income and sales.
The Potential of Artificial Intelligence for the Manufacturing Sector
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) spans the whole production cycle, from sourcing raw materials to shipping finished goods. Predictive maintenance is where AI shines. Businesses in the manufacturing sector may improve machine failure prediction and prevention by using AI to produce data. As a result, production downtime is reduced, saving money. Other applications of AI in production include more accurate demand forecasting, heightened quality control, enhanced inspections, and automated stockroom.
“Industry 4.0,” the movement toward more automation in manufacturing plants and the massive creation and transfer of data, relies heavily on artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are essential to help businesses make sense of the massive volumes of data produced by industrial equipment. Saving money, making the workplace safer, and streamlining the supply chain are just a few of the many potential outcomes of applying AI to this information.
Machine learning and deep learning, natural language processing, and machine vision are just a few of the AI sub-technologies that play an important part in many manufacturing tasks.
[To share your insights with us, please write to sghosh@martechseries.com]

Comments are closed.